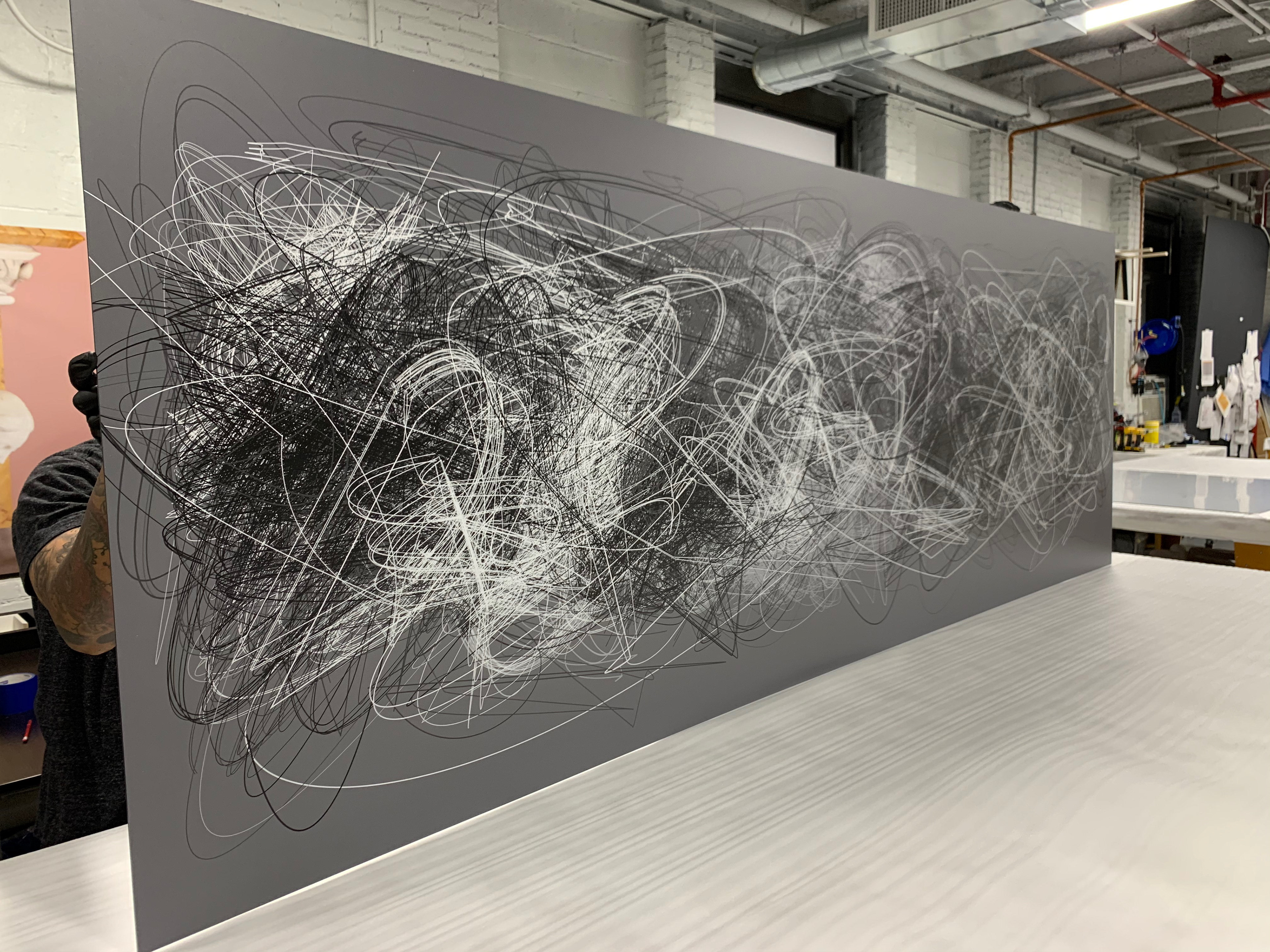
These Paintings are composed from the altered text of a list of the names of all the stars visible in the night sky.
Astrolabes were used in classical antiquity, the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery as a tool for navigating by the stars. An astrolabe consists of a disk, called the mater (mother), which is deep enough to hold one or more flat plates called tympans, or climates. A tympan is made for a specific latitude and is engraved with a stereographic projection of circles denoting azimuth and altitude and representing the portion of the celestial sphere above the local horizon.
Astrolabe uv polymer on canvas 69 x 189 in 2015
Astrolabe 3 uv polymer on aluminum 38 x 106 in 2020
Astrolabe [state 3] uv polymer on aluminum 40 x 93 in 2020